Newsetter vol.2 アメリカでのIoTの状況
ライアン・キャロル
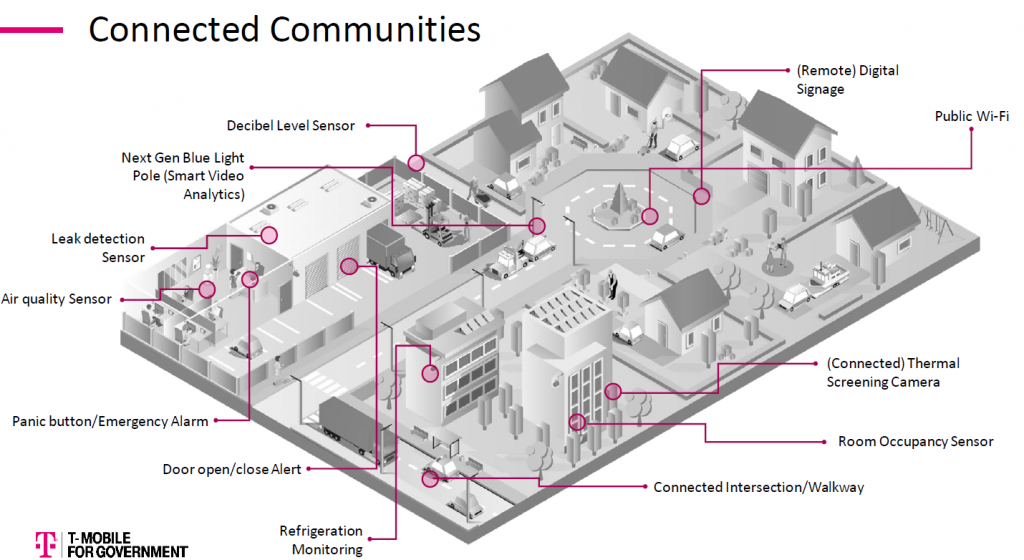
IoT(Internet of Things)とは,あらゆる機器やアプリケーションをインターネットや他の接続機器に接続するという概念であり,今日の現代経済において広く普及しているトピックである.IoTは接続されたモノや人の広大なネットワークを表し,これらのエンドポイントはすべてデータを収集・共有し,効率化と接続性の向上を図っている.これらの接続されたエンドポイントは非常に多様で,食器洗い機のようなスマート家電から自動運転自動車,生体認証ウェアラブルに至るまで,あらゆる分野に及んでいる.また,ゴミ箱にSIMセンサーを搭載し,ゴミ箱の中の状態を監視し,満杯になれば衛生局に回収を依頼するものもある.
このようなセンサーが組み込まれたデバイスは,Internet of Thingsプラットフォーム(Cisco Jasper Control Centerなど)に接続される.異なるデバイスからのデータを統合して,最も実用的な情報を解析し,特定のニーズに対応するために分析を適用する.Cisco Jasperプラットフォームを例にとると,何千もの携帯電話対応IoTデバイスの接続を1つのグローバルなSaaS(Software as a Service)ソリューションで管理している.エンドユーザーは,接続されたデバイスをほぼリアルタイムで展開,管理,監視することができる.今日のデータ駆動型の環境では,企業は無駄を省き,環境に配慮することが求められている.自動化された接続プラットフォームにより,携帯電話のデータ使用量の監視やエネルギー消費の削減とコスト管理のための通知を行うことができる.さらに企業は,プロセスの効率化,規制遵守,多層的なセキュリティに役立つIoT対応ソリューションの利点を認識しつつある.
おそらく最も有用な産業用IoTの使用例は,資産の稼働を維持し,運用経費を大幅に削減する可能性を持つ予知保全である.センサー,カメラ,データ分析を使用することで,管理者は実際に故障が発生する前に,機器の故障時期を判断することができる.これらのIoT対応システムは,警告の兆候を検知・解釈し,診断を適用してパフォーマンスを回復させ,問題が発生する前に先手を打って機器を修理することができる.このシナリオにおいてIoTを活用することにより,機器の寿命が延び,プラントの安全性が向上し,機器と従業員の両方が関わる事故が減少するなどの利点も期待できる.
今日,モノのインターネットは,ビジネスの運営方法と相互の競争において,抜本的な変革を促している.あらゆる規模の,ほぼすべての分野の企業が,IoTを活用して,コスト,複雑性,スケーリングの課題に対処している.2025年までに,IoTデバイスは300億個になると予想されており,これは地球人1人当たりほぼ4個のデバイスが存在することになる. 車両管理,資産管理,在庫管理,自動販売機など,あらゆる場面で,携帯電話ネットワークに接続されたIoTプラットフォームによる業務効率化とコスト削減が期待されている.特に,通信事業者が高速で信頼性の高い5Gネットワークを展開し,低遅延で大規模なアプリケーションの接続をサポートできるようになった現在では,さらなる進化が期待できる.
The Internet of Things (IoT) in the US
Ryan Carroll
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a prevalent topic in today’s modern economy and is the concept of connecting any device or application to the Internet, as well as to other connected devices. IoT represents a sprawling network of connected things and people; all of these endpoints collect and share data to drive efficiencies and improve connectivity. These connected endpoints are incredibly diverse and run the gamut from smart appliances like dishwashers, to self-driving automobiles and biometric wearables. There are even trash bins equipped with SIM -enabled sensors that monitor when the bins fill up, and then alert the sanitation department for pickup.
Devices with such embedded sensors are typically connected to an Internet of Things platform (e.g., Cisco Jasper Control Center), which amalgamates data from different devices and applies analytics to parse the most actionable information and address specific needs. Taking the Cisco Jasper platform for example, it manages the connectivity of thousands of cellular-enabled IoT devices in one global software as a service (SaaS) solution. The end-user can deploy, manage, and monitor their connected devices in near real-time. In today’s data-driven environment where companies seek to be less wasteful and more environmentally conscious, automated connectivity platforms allow for cellular data usage monitoring, and notifications to lessen energy consumption and manage costs. Additionally, companies are realizing the benefits of IoT-enabled solutions that can help process efficiency, regulatory compliance, and multi-layered security.
Perhaps the most useful industrial IoT use case is predictive maintenance, which involves keeping assets up and running and has the potential to greatly decrease operational expenditures. Using sensors, cameras, and data analytics, managers can determine when a piece of equipment will fail before it actually does. These IoT-enabled systems can detect and interpret warning signs, apply diagnostics to restore performance, and preemptively service equipment before problems occur. Other potential advantages of leveraging IoT in this scenario include increased equipment lifetime, better plant safety, and fewer accidents involving both equipment and employees.
Today, the Internet of Things is driving radical transformation in how businesses operate and compete with one another. Companies of all sizes, from nearly every sector, are leveraging IoT to address cost, complexity, and scaling challenges. By 2025, there are expected to be 30 billion IoT devices – almost 4 devices per person on Earth. Whether a company is looking to implement fleet and asset management, or manage inventory and automate vending in retail, it would behoove business leaders to unlock operational efficiencies and cost savings through an IoT platform connected to a cellular network. Especially, now that carriers are rolling-out fast, reliable 5G networks that can support low-latency and massive connectivity of applications.
Ryan Carroll ライアン・キャロル
Ryan Carroll works for T-Mobile in Seattle, Washington where he specializes in telecommunications and IoT solutions for government agencies and nonprofit institutions. Prior to working at T-Mobile, he worked in sales at AT&T where led the company’s efforts in Washington and Idaho. Here, he managed numerous wireless projects such as distributed antenna systems, private networking solutions, and traditional mobility. Ryan attended the University of Chicago as an undergraduate and then earned his Master’s Degree in German and International Business at Georgetown University, where he wrote his thesis on the European Union’s telecommunications and aviation market. He currently lives in Seattle with his wife, son, and dog Tenley.

